
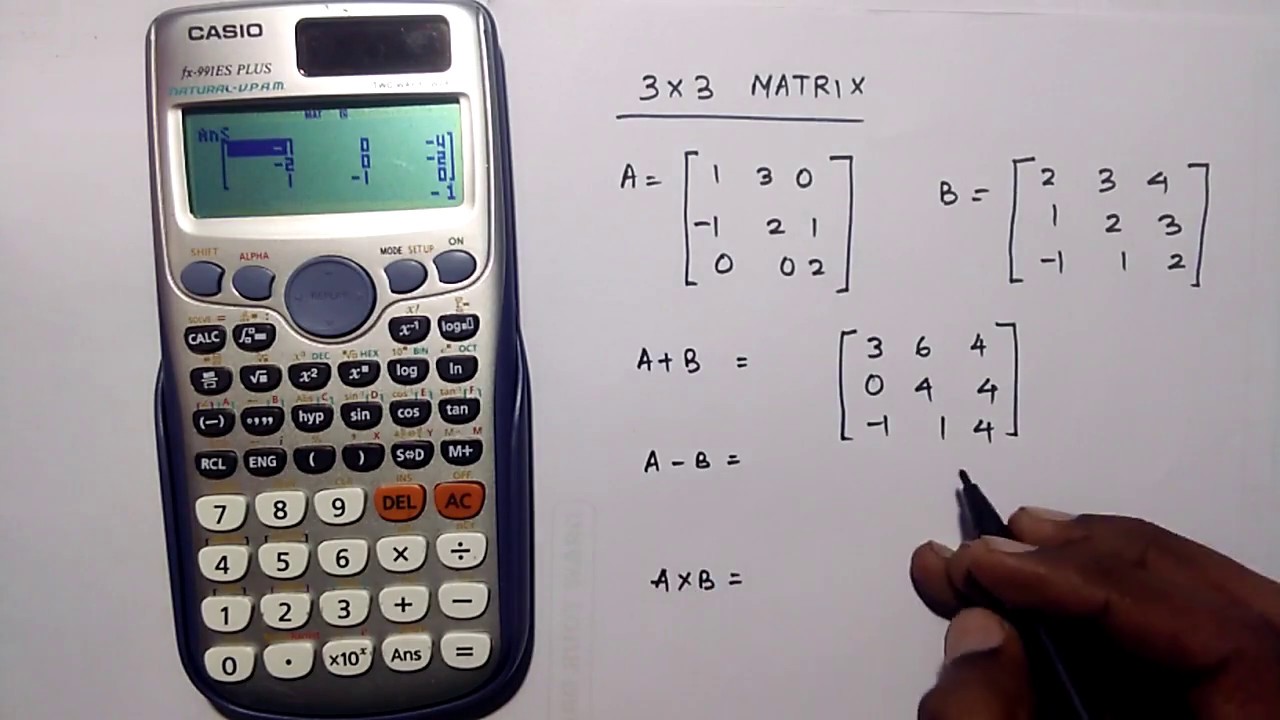
You transpose the coordinates from matrix A to matrix B, for a linear transformation from one coordinate system to another in a product matrix. One common application of multiplying matrices is in the transformation between coordinate systems where the matrix is the coordinates of unit vectors from one coordinate system in another. The applications of matrix and scalar multiplication are endless. When you multiply these two matrices in an element by element manner you get the total number of miles that each vehicle will go on a single tank of gas. Likewise, each column refers to the model in each row refers to the engine. The other would be the mileage that each model car gets with each size engine. Each column refers to the model in each row refers to the engine. One would be the size gas tank each model has for each engine size in gallons. Element wise multiplication takes each column vector and row vector and multiplies them together to get the matrix vector product. ApplicationsĪ good example of an element by element matrix multiplication equation is the one used above of three models of cars that share three size motors of the same type. If you inverse the order of the original matrix and the second matrix, the result matrix will be slightly different than the matrix product of the first operation. The original matrix and the second matrix are each identified by a matrix multiplication operator, and are combined for a result of the product matrix. Note that the order of the matrices affects the results in matrix multiplication. This operation does a simple element by element multiplication up to matrices. The first is denoted by * which is the same as a simple multiplication sign. R has two multiplication operators for matrices.
Multiplying matrices using a multiplication operator in R is one of a massive array of matrix operations and matrix algebra you can perform in R. Now, the columns, or rows can be omitted, and they will be calculated by R, however, the one given needs to be a multiple of the total number of elements. Now, the number of rows multiplied by the number of columns must equal the total number of elements in the vector. Creating a matrix in R is quite simple, it involves the Matrix function that has the format of matrix(vector, ncol=columes, nrow=rows2) and it takes the vector and converts it to specified number of rows and columns.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
